This article puts samesum_log2_norm() and
samesum_log2_cpm() through their paces.
Example usage
lnorm <- samesum_log2_norm(counts)
colSums(lnorm)
#> untrt1 trt1 untrt2 trt2 untrt3 trt3 untrt4 trt4
#> 123445.8 123445.8 123445.8 123445.8 123445.8 123445.8 123445.8 123445.8
attr(lnorm,"sum")
#> [1] 123445.8
attr(lnorm,"samples")
#> name scale true_lib_size adjusted_lib_size
#> 1 untrt1 2.006479 20637971 21667160
#> 2 trt1 1.760615 18809481 19012176
#> 3 untrt2 2.424240 25348649 26178399
#> 4 trt2 1.293811 15163415 13971346
#> 5 untrt3 2.342422 24448408 25294871
#> 6 trt3 2.778465 30818215 30003524
#> 7 untrt4 1.861340 19126151 20099863
#> 8 trt4 1.833587 21164133 19800165
plot_heatmap(
lnorm,
feature_labels=rowData(airway)$symbol,
n=50, baseline_to=0)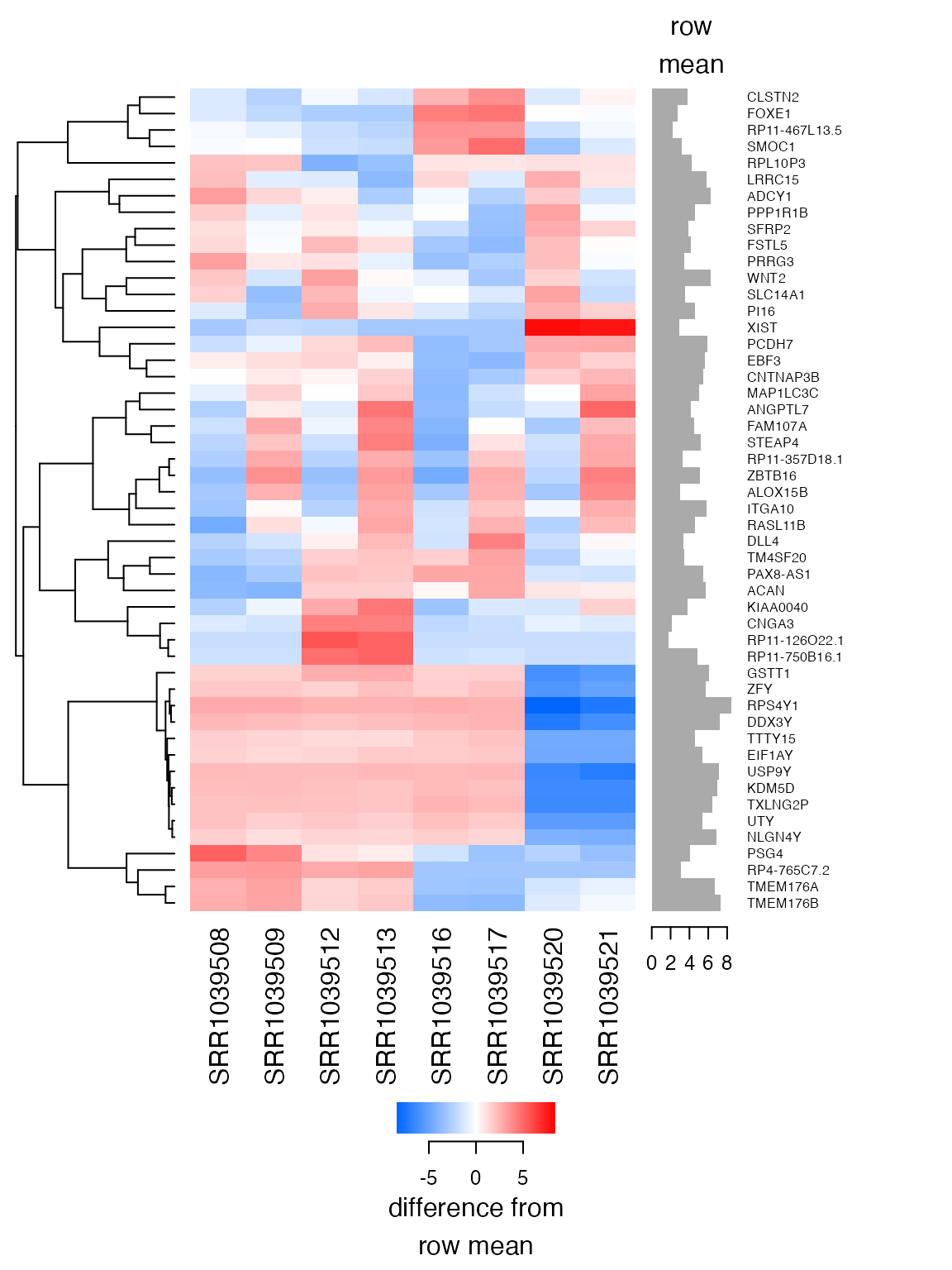
plot_biplot(lnorm, feature_labels=rowData(airway)$symbol)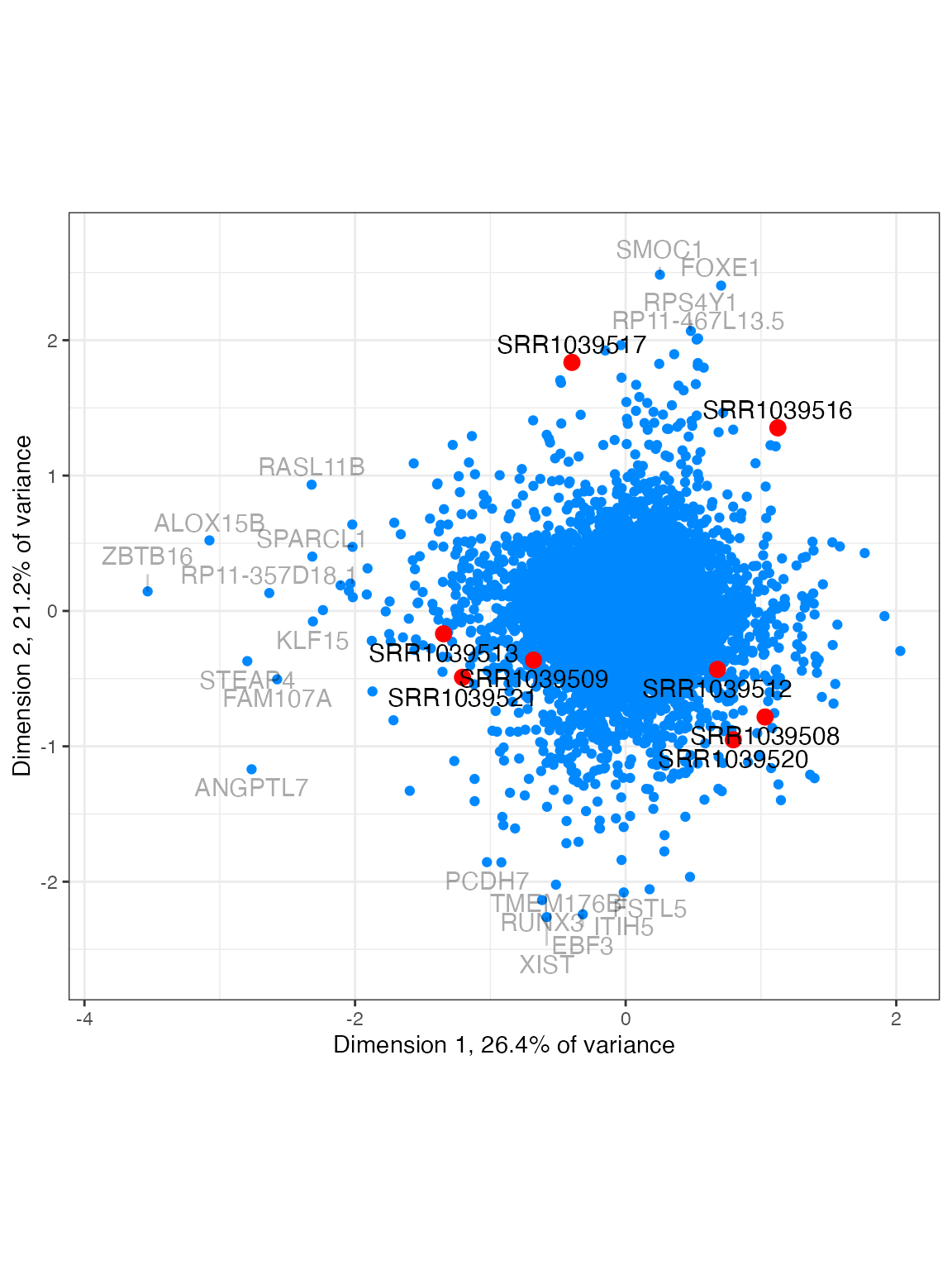
Filtering
Some analysis methods don’t work well with features that are nearly all zero. In particular we suggest filtering before using limma. However samesum transformation works fine with very sparse data, so we suggest transforming your data before filtering it. This allows filtering to be applied fairly across samples with different scale values.
Here the data has four replicates per treatment group, so for each
gene I require some level of expression in at least four samples. This
is similar to the strategy used by edgeR::filterByExpr.
keep <- rowSums(lnorm >= 2.5) >= 4
table(keep)
#> keep
#> FALSE TRUE
#> 47530 16147
lnorm_filtered <- lnorm[keep,]
design <- model.matrix(~ 0 + dex + cell, data=colData(airway))
plot_stability(lnorm_filtered, counts[keep,], design=design)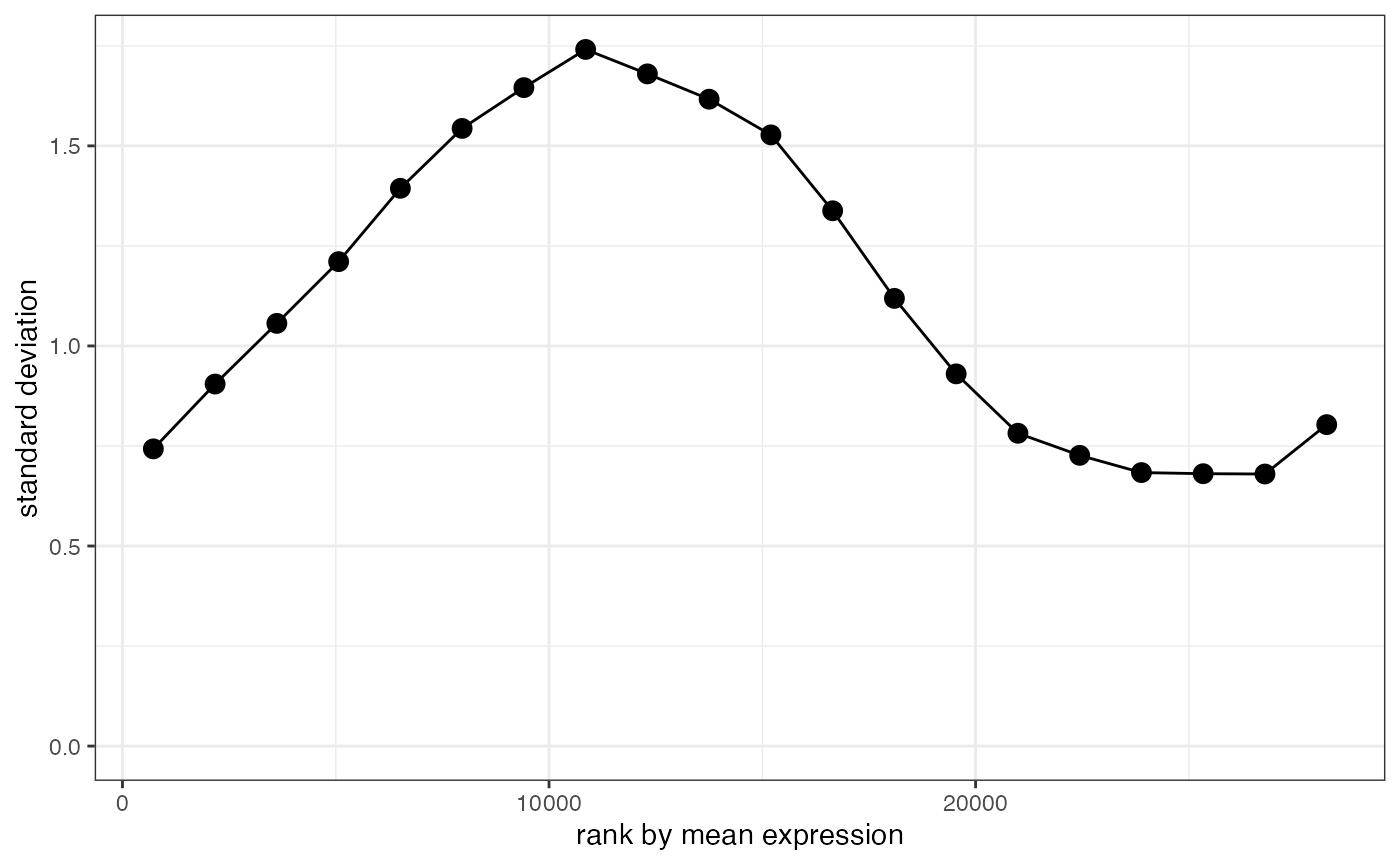
You can provide a larger target scale for greater variance stabilization
The default target scale parameter is 2, which may produce noisy results for features with low abundance. This scale parameter can be increased.
lnorm_10 <- samesum_log2_norm(counts, scale=50)
colSums(lnorm_10)
#> untrt1 trt1 untrt2 trt2 untrt3 trt3 untrt4 trt4
#> 48190.48 48190.48 48190.48 48190.48 48190.48 48190.48 48190.48 48190.48
attr(lnorm_10, "samples")
#> name scale true_lib_size adjusted_lib_size
#> 1 untrt1 50.13240 20637971 21644530
#> 2 trt1 44.35235 18809481 19149007
#> 3 untrt2 58.64445 25348649 25319585
#> 4 trt2 33.46828 15163415 14449840
#> 5 untrt3 57.53114 24448408 24838916
#> 6 trt3 69.50408 30818215 30008201
#> 7 untrt4 45.59064 19126151 19683636
#> 8 trt4 47.37619 21164133 20454544
keep_10 <- rowSums(lnorm_10 >= 0.25) >= 4
table(keep_10)
#> keep_10
#> FALSE TRUE
#> 47552 16125
lnorm_10_filtered <- lnorm_10[keep_10,]
plot_stability(lnorm_10_filtered, counts[keep_10,], design=design)
You can provide the target sum directly
By default, samesum_log2_norm chooses the target sum
based on the average sum from a first pass transformation of the data
with the target scale. You might instead provide this target sum
directly.
lnorm_sum <- samesum_log2_norm(counts, sum=1e5)
colSums(lnorm_sum)
#> untrt1 trt1 untrt2 trt2 untrt3 trt3 untrt4 trt4
#> 1e+05 1e+05 1e+05 1e+05 1e+05 1e+05 1e+05 1e+05
attr(lnorm_sum, "samples")
#> name scale true_lib_size adjusted_lib_size
#> 1 untrt1 4.711026 20637971 21695573
#> 2 trt1 4.132692 18809481 19032182
#> 3 untrt2 5.624991 25348649 25904631
#> 4 trt2 3.077556 15163415 14172993
#> 5 untrt3 5.449664 24448408 25097201
#> 6 trt3 6.483651 30818215 29858998
#> 7 untrt4 4.344943 19126151 20009660
#> 8 trt4 4.346977 21164133 20019024For example you might want to ensure the chosen scale for each sample
is greater than some minimum. You could compute the first pass sums
yourself with colSums(log1p(counts/target_scale))/log(2)
and provide the minimum value as the target sum.
I propose to call the units of the target sum “dublins”, being roughly how many doublings of abundance are observed in each sample. You can think of this as the resolution at which we are looking at the data. Now we generally want the scale to be greater than, say, 0.5, and this will mean different technologies and sequencing depths will support different amounts of dublins.
If comparing multiple datasets, using a consistent target sum allows for consistent comparisons. For example the sum of squared log fold changes minus the sum of squared standard errors can be used as an unbiassed estimate of how much differential expression there is between two conditions. To render this consistent across multiple disparate datasets, a consistent number of dublins could be used.
You can also produce log2 CPM values
Counts Per Million (CPM) is a widely used unit for RNA-Seq data, so I
also provide a function to produce results in log2 CPM units. This is
quite similar to edgeR’s cpm function with
log=TRUE.
lcpm <- samesum_log2_cpm(counts)Zeros will no longer be zero. This is fine, log transformation is meant to transform positive values to cover the whole real line. It is convenient sometimes to pick a log transformation with a pseudocount that transforms zeros to zero, but it is not necessary.
You can check the value that zeros are transformed to.
min(lcpm)
#> [1] -3.434502
attr(lcpm, "zero")
#> [1] -3.434502
mean(colSums(2^lcpm-2^attr(lcpm,"zero")))
#> [1] 1e+06Adjust your filtering appropriately.
Low library size samples produce a warning
Here I have downsampled the first sample to 1% of the original. The function gives a warning.
set.seed(563)
counts_sub <- counts
counts_sub[,1] <- rbinom(nrow(counts_sub), counts_sub[,1], 0.01)
lnorm_sub <- samesum_log2_norm(counts_sub)
#> Warning in samesum_log2_norm(counts_sub): 1 samples have been given a scale
#> less than 0.5. These may subsequently appear to be outliers as an artifact of
#> the transformation. Consider using a larger target scale or excluding these
#> samples from analysis.You can examine the samples attribute for more details.
attr(lnorm_sub,"samples")
#> name scale true_lib_size adjusted_lib_size
#> 1 untrt1 0.0103538 205717 83191.73
#> 2 trt1 2.7133387 18809481 21801392.68
#> 3 untrt2 3.7132470 25348649 29835551.65
#> 4 trt2 2.0091857 15163415 16143596.90
#> 5 untrt3 3.5924834 24448408 28865228.65
#> 6 trt3 4.2665191 30818215 34281035.59
#> 7 untrt4 2.8609935 19126151 22987783.61
#> 8 trt4 2.8410567 21164133 22827594.11Sample 1 is indeed an outlier now, and this is purely an artifact of the transformation:
plot_heatmap(lnorm_sub, feature_labels=rowData(airway)$symbol, n=50, baseline_to=0)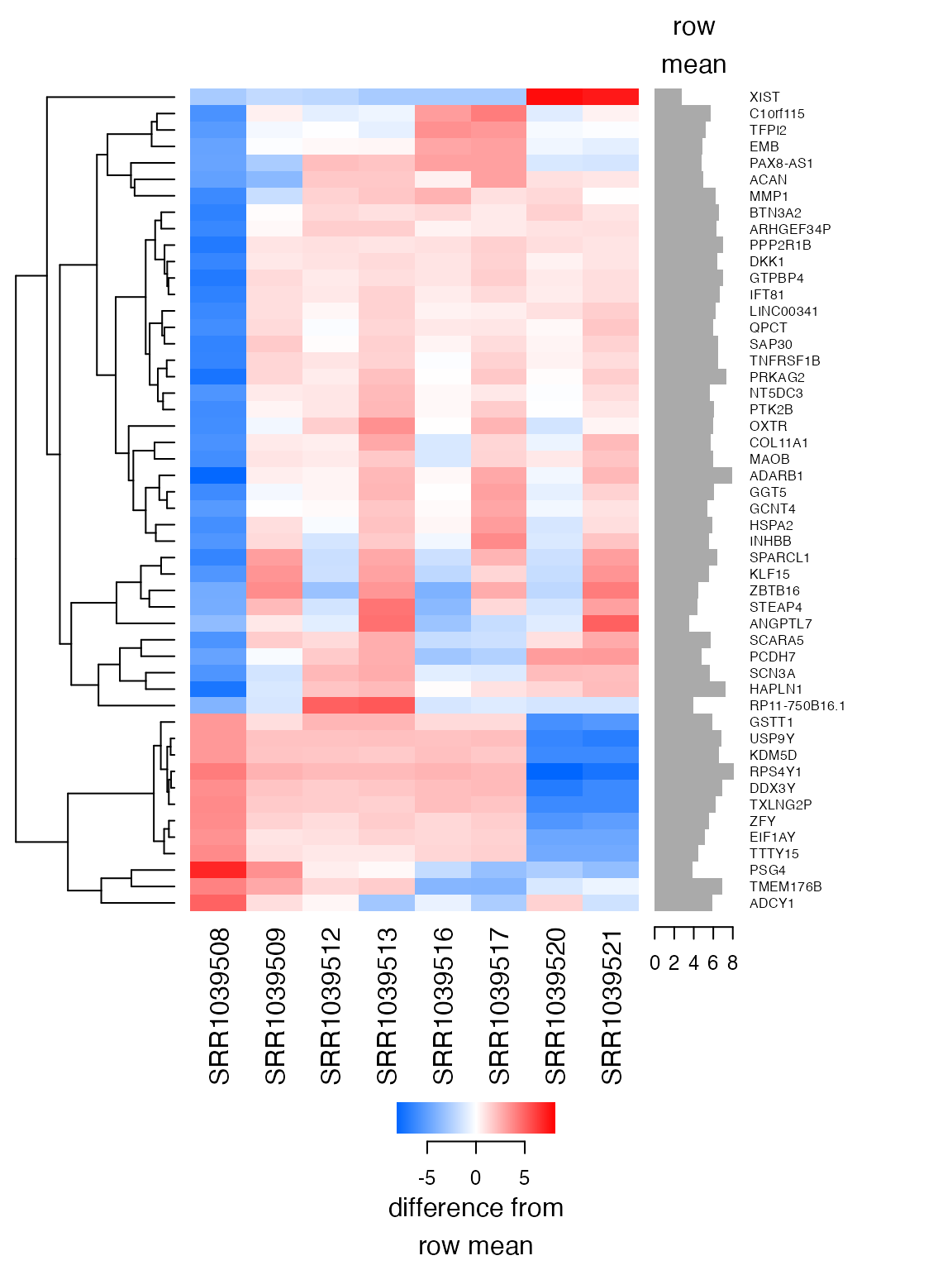
Increasing the scale parameter removes the warning and
fixes the problem. The cost is that we squash variability in genes with
low expression levels. It’s like we’ve reduced the “resolution” of the
data.
lnorm_sub_200 <- samesum_log2_norm(counts_sub, scale=200)
attr(lnorm_sub,"sum")
#> [1] 111245.9
attr(lnorm_sub_200,"sum")
#> [1] 23743.31We’re now looking at the data at a resolution of 23,743 dublins, where previously we were looking at a resolution of 111,246 dublins.
plot_heatmap(lnorm_sub_200, feature_labels=rowData(airway)$symbol, n=50, baseline_to=0)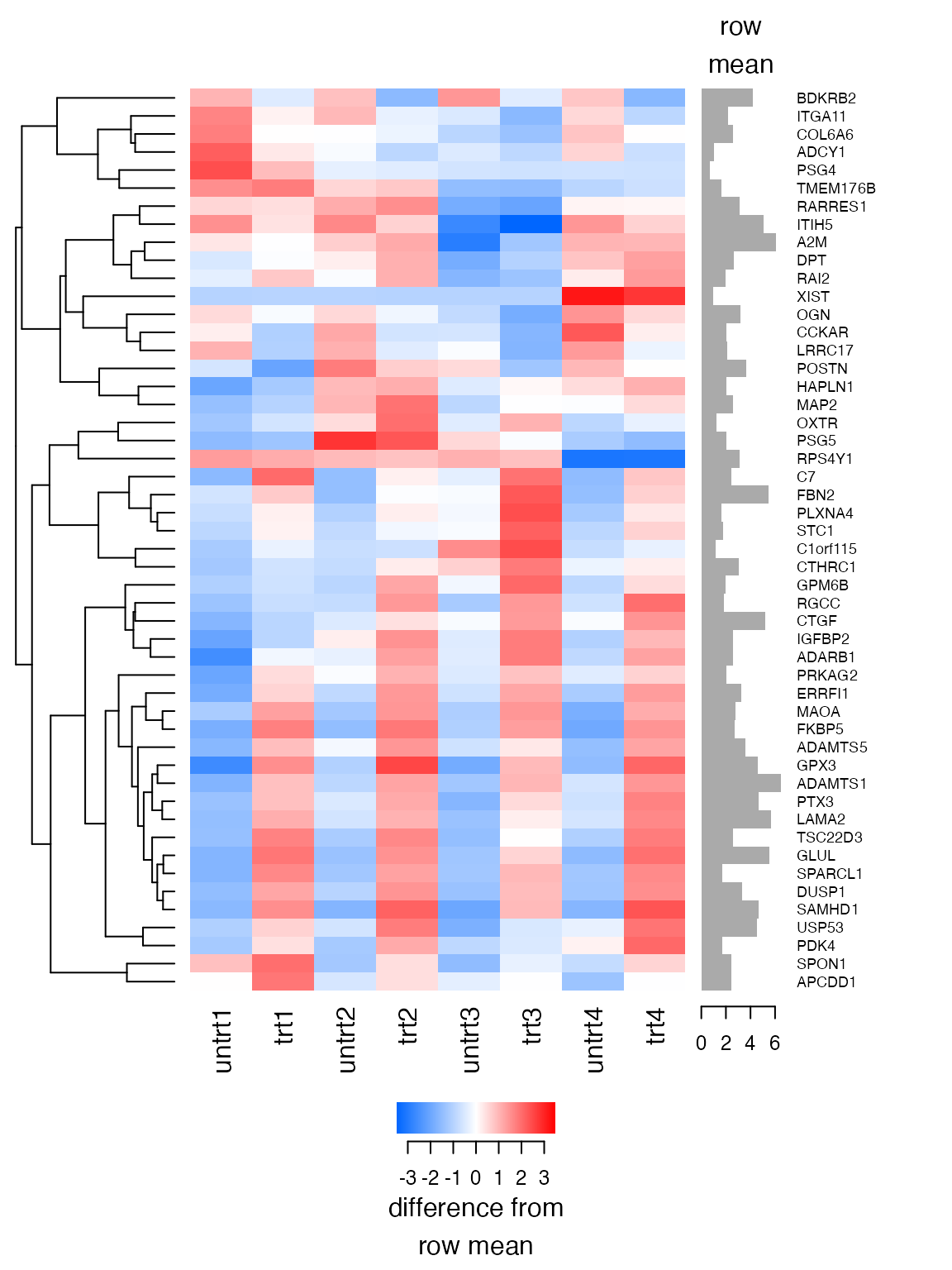
You will also get a warning if a sample is all zero.
counts_zeroed <- counts
counts_zeroed[,1] <- 0
lnorm_zeroed <- samesum_log2_norm(counts_zeroed)
#> Warning in samesum_log2_norm(counts_zeroed): 1 samples are entirely zero.Or sometimes a sample has very low library size or complexity, and the scale underflows to zero.
counts_low <- counts_zeroed
counts_low[1,1] <- 1
lnorm_low <- samesum_log2_norm(counts_low)
#> Warning in samesum_log2_norm(counts_low): 1 samples where the scale has
#> underflowed and been given a value of zero. Please remove these samples.Sparse matrices can be used
samesum_log2_norm transforms zeros to zeros, so the
matrix remains sparse. This can be useful for example with scRNA-Seq
data.
counts_sparse <- Matrix( assay(airway, "counts") )
lnorm_sparse <- samesum_log2_norm(counts_sparse)
class(lnorm_sparse)
#> [1] "dgCMatrix"
#> attr(,"package")
#> [1] "Matrix"